Jamaica. ‘Don’t Worry, Be Happy’.

This year Jamaica is celebrating 60 years of independence from the United Kingdom. A country that is constantly living in a political and economic crisis. High crime rate. It is one of the most important cannabis producers. Reggae music.
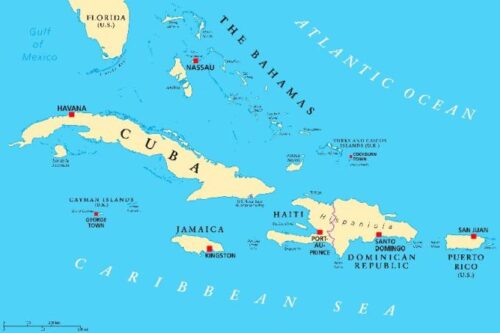
The island of Jamaica, located in the Caribbean Sea, belongs to the Greater Antilles Archipelago. The location gives the island great strategic importance: its northern coast is 145 km from Cuba and the eastern coast about 190 km from Haiti; from the capital, Kingston, across the Caribbean Sea, to the mouth of the Panama Canal, is a distance of 938 km. Its territory is mainly mountainous while not exceeding 1,000 meters above sea level. An exception to this is the chain of the Blue Mountains, located on the eastern side of the island, whose peaks reach 2,256m in height and extend for about 50 km. The few plains present on the island can be found in the southern coastal strip, while the coasts of the northern strip are more rugged and elevated. Small islands located in the southern coastal strip also belong to the territory of the country, the dimensions of which, however, are quite modest.

123rf.com
There are numerous water sources on the island and, in the opinion of some scholars, the name Jamaica derives from a corruption of the name ‘Arawak Xaymaca’ alluding to them. Furthermore, the island is crossed by a hundred rivers whose length, due to the arrangement of the mountain ranges, does not exceed 100 km. Among these is the Rio Minho which, at 93 km, is the longest river in Jamaica. It rises near the geographic centre of the island, flows generally south-southwest and reaches the Caribbean Sea at Carlisle Bay on the south-central coast, west of the island’s southernmost point, Portland Point. While the Black River, whose name refers to the darkness of its bed caused by thick layers of decaying vegetation, flows for about 53 km west and then flows into the Caribbean Sea, near Negril.
The climate is tropical and is generally hot and humid. With the exception of the higher and temperate areas, temperatures undergo decidedly limited seasonal variations and the average maximums in the capital vary from 30 ° to 33 ° C, with minimums from 21 ° to 24 ° C. Precipitation is quite consistent in the hinterland and, in particular, in mountainous areas where it reaches peaks of 5,000-6,000 mm every year. On the other hand, it is less in the coastal strip and, in particular, in the southern one, where it may reach as little as 800 mm per year. The country is also in an area frequently struck by hurricanes.
The discovery of the island took place on May 3, 1494 by Christopher Columbus who called it Santiago. At that time the island was already inhabited by the Arawaks, a population originally from South America who had settled there between 1000 and 400 BC. They died out at the end of the sixteenth century due both to the hard work imposed by the colonists and the European ill-treatment and diseases against which they had no defence.

In fact, the Spanish colonists, who arrived on the island beginning in 1510, introduced slavery together with the cultivation of sugar cane, thus modifying the layout of the island.In 1597 the English raids began though they managed to obtain effective control only in 1654. Under English domination, Jamaica became the first nation in the world for sugar exports thanks to the massive use of slaves imported from Africa. The insurrections of the latter, however, were constantly transforming, with the passage of time, into actions by guerrillas whose attacks forced the British to grant them a greater degree of autonomy in 1739. But, despite these concessions, the struggles continued in a very bloody manner even in the following decades. In particular, at Christmas 1831 an action of passive resistance infused by Daddy ‘Sam’ Scarpe, an educated slave and lay preacher, took on the character of extreme violence resulting in the destruction of the landowners’ plantations which ended with the hanging of about 400 rioters. This caused a wave of outrage in England itself that eventually forced parliament to abolish slavery on August 1, 1834.

@KhosroKalbasi 123rf.com
Although this system was abolished, the government of the rich, who were the only ones with the right to vote, maintained its political weight. The slaves freed from slavery at that point abandoned the work of the plantations and settled on the island and this, in addition to causing economic decline due to lack of manpower, generated new struggles with the ancient masters that persisted over time.
In the history of the country, an undoubtedly important date was 1958, the year in which the island acquired its first independence from the United Kingdom, becoming a province belonging to the Federation of West Indies, that is, an organization in which all the British West Indies took part. However, full independence came on August 6, 1962 with the separation from the Federation of West Indies and the United Kingdom while remaining within the Commonwealth and joining the UN and the OAS. In the years that followed there was a policy of alternating between Labour and Nationalists, the latter led by M. Manley. The economic and social conditions of the country recorded continuous and constant worsening with organized crime acquiring ever greater room for manoeuvre thanks also to collusion between the political class and the various gangs that faced each other and were duly armed by Kingston.
Jamaica, which today has 2,961,000 inhabitants, is the third most populous English-speaking country in the Americas, after the USA and Canada. Its population is mainly composed of descendants of populations from the sub-Saharan area and enslaved by the British.(Photo: 123rf.com) – (F.R.)



